
 Intel® Optane™ Memory is a revolutionary class of memory that bridges the gap between DRAM and storage to boost the overall performance of client PCs which includes desktops, small form factor systems, AIOs, notebooks, and other mobile solutions. Intel® Optane™ Memory is designed to act as a cache for the hard drive. Cache is not a new concept, but Intel® Optane™ Memory offers several advantages over traditional cache technologies. Mainly previous cache technologies proved to have too small of capacity, the memory was volatile and too slow, as well as it was very costly. Intel® Optane™ memory is a four lane M.2 PCIe 3.0 connection that utilizes 3D Xpoint Technology which is 10X faster than traditional NAND and is 10X denser than DRAM so when paired with a standard HDD system performance is improved by over 28%. The obvious benefit is that resellers can offer their clients PCs with Intel® Optane™ Memory and spinning HDD to deliver a system that has near SSD performance at a lower cost as well as having the storage capacity of disk drives.
Intel® Optane™ Memory is a revolutionary class of memory that bridges the gap between DRAM and storage to boost the overall performance of client PCs which includes desktops, small form factor systems, AIOs, notebooks, and other mobile solutions. Intel® Optane™ Memory is designed to act as a cache for the hard drive. Cache is not a new concept, but Intel® Optane™ Memory offers several advantages over traditional cache technologies. Mainly previous cache technologies proved to have too small of capacity, the memory was volatile and too slow, as well as it was very costly. Intel® Optane™ memory is a four lane M.2 PCIe 3.0 connection that utilizes 3D Xpoint Technology which is 10X faster than traditional NAND and is 10X denser than DRAM so when paired with a standard HDD system performance is improved by over 28%. The obvious benefit is that resellers can offer their clients PCs with Intel® Optane™ Memory and spinning HDD to deliver a system that has near SSD performance at a lower cost as well as having the storage capacity of disk drives.
Since their launch Intel has introduced several iterations of Intel® Optane™. The original product was Intel® Optane™ Memory offered in a 16GB or 32GB M.2 2280 PCIex2 module. The next generation released is Intel® Optane™ Memory M10 which offers several advantages over the original Intel® Optane™ Memory. Also based on the M.2 2280 PCIe x 2 form factor the M10 version brings an additional cache capacity so it is available in 16GB, 32GB and 64GB. In addition Intel® Optane™ Memory M10 can cache a secondary data drive whereas the original could only cache the boot drive. Another advantage on the M10 is that it was designed for use in mobile devices as well as desktops so it has improved power management. Following the M10 is Intel® Optane™ Memory M15 which is the same as M10 except M15 is a M.2 2280 M Key only so it uses a PCIex4 interface increasing the throughput capacity and improving performance. The note here is that Intel® Optane™ Memory M15 requires a motherboard with a PCIex4 M.2 connection.
In terms of performance the best solution is the Intel® Optane™ Memory M15 because it is supported by the higher throughput of PCIex4 compared to PCIex2 used on the original Intel® Optane™ Memory and the M10. The M10 demonstrates higher performance ratings due to the comparison of the larger 64GB cache. Similar cache sizes should perform the same between Intel® Optane™ Memory and Intel® Optane™ Memory M10.
All Intel® Optane™ Memory versions require an Intel 7th Generation or newer processor and the installation of Intel Rapid Storage Technology software so although this performance boosting option is not available to users with older PCs it is an excellent value add for any new system.
| Model | Optane Memory M15 | Optane Memory M10 | Optane Memory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Form Factor | M.2 2280 M key | M.2 2280 B+M key | M.2 2280 B+M key |
| Interface | PCIe 3.0 x4 | PCIe 3.0 x2 | PCIe 3.0 x2 |
| Capacities | 16 GB, 32 GB, 64 GB | 16 GB, 32 GB, 64 GB | 16 GB, 32 GB |
| Memory | 128Gb 20nm Intel 3D XPoint | 128Gb 20nm Intel 3D XPoint | 128Gb 20nm Intel 3D XPoint |
| Sequential Read | Up to 2,000 MB/s | Up to 1,450 MB/s | Up to 1,350 MB/s |
| Sequential Write | Up to 900 MB/s | Up to 640 MB/s | Up to 290 MB/s |
| Random Read (QD4) | Up to 450k IOPS | Up to 250k IOPS | Up to 240k IOPS |
| Random Write (QD4) | Up to 220k IOPS | Up to 140k IOPS | Up to 65k IOPS |
| Endurance | 365 TB | 365 TB | 182.5 TB |
| Warranty | 5 years | 5 years | 5 Years |
Intel® Optane™ Memory H10
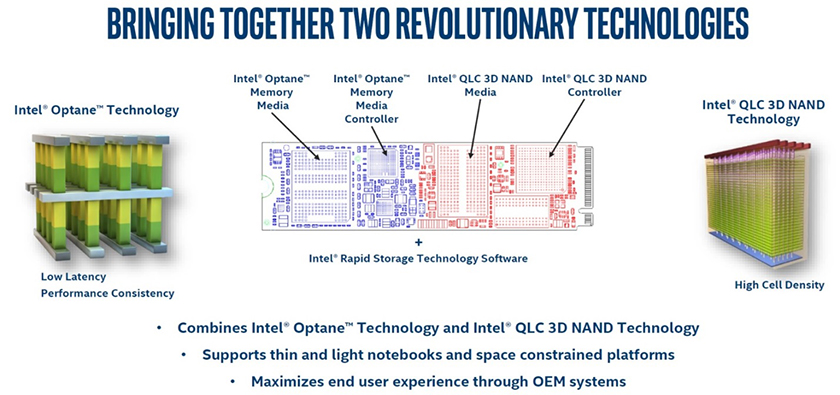
Intel® Optane™ Memory H10 is essentially a hybrid SSD product that fuses two Intel Technologies on to one M.2 PCIe x 4 device. The SSD solution includes Intel® Optane™ Memory functioning as cache combined with the Intel 660P SSD functioning as storage. The benefit of combining these products together is that consumers can now further improve the performance of their SSD through the addition of 3D Xpoint memory which Intel brands as Optane. The storage and caching combination is available in several flavors with the cache being either 16GB or 32GB and the storage being 256GB, 512GB or 1TB.
With this concept Intel is essentially combining two PCIe x 2 products on to one M.2 form factor so the device internally bifurcates the PCIe x4 lane into two PCIe x 2 lanes, one for the Intel® Optane™ Memory cache and the other for the Intel 660P. Managing this setup makes integrating the H10 more complex than simply adding the module to a system. There are differing considerations that include chipset compatibility, MB compatibility, proper M.2 slot configuration, proper BIOS, proper Windows drivers, proper MB firmware, as well as the correct Intel RST driver and of course proper setup of the entire configuration. It is for these reasons that the H10 is not intended to be sold as a standalone device and is intended to be integrated by the reseller or by ASI.
Reseller Advantage
For VARs that are building and branding their own PC, the Intel® Optane™ Memory H10 solution can offer several advantages. First and foremost, integrating the H10 requires knowledge and expertise which cannot be delivered by simply purchasing the H10 online or as a standalone device. This product must be integrated as part of a new PC. Additionally MNCs are primarily using the technology in performance series notebooks so making the solution available in a desktop is a clear advantage that VARs can deliver. Lastly, VARs can provide their customer with another solution that will further boost the performance of their PC for everyday computing which ultimately adds another level of differentiation to distinguishes their brand.
Customer Benefit
Although Intel® Optane™ Memory was originally introduced as a solution to improve the performance of systems that used spinning disks, it also offers benefits to systems that use SSD particularly in real-world usage scenarios where users are typically engaged in performing mixed reads and multitasking at low que depth. In other words, the most common tasks performed by typical users involve 70% read and 30% write. as well as include opening up to 62 applications a day which may run in the background. Such low que depth applications include word, excel, Acrobat, Outlook, Photoshop Elements, and Power Point. With such high use of read functions, utilizing cache will have a profound impact on the performance of the system.

