Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor and 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor
Intel’s hybrid processor architecture which integrates both performance and efficiency cores on the same processor is a technology utilized in the Intel Core Processor (14th Gen) code named Raptor Lake Refresh, the 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor, code named Raptor Lake, and the 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor, code named Alder Lake. These processors offer superior gaming performance while delivering the flexibility to seamlessly multitask. Innovative new architecture matches the right core to the right workload, so background tasks won’t interrupt your game. Giving you the freedom to chat, browse, stream, edit, record, and play without skipping a beat.
With the new processors there comes many advanced technologies as well as new components including the CPU, chip set, motherboard, CPU socket, cooling fan, memory and more. To help customers we have created this interactive resource to assist in learning about these new technologies and identifying ASI SKUs. Simply mouse over the buttons on the motherboard image to learn more.
Please click a circle on the motherboard to see more information

Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor and 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor - More Info

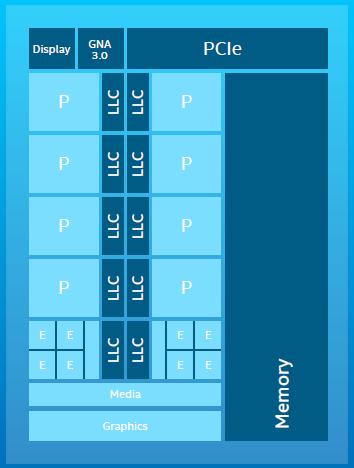
Based on a new socket, LGA1700, the 14th, 13th and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ desktop processors, code named Raptor Lake Refresh, Raptor Lake and Alder Lake, powers a revolutionary approach to x86 architecture. Utilizing a hybrid design, these processors incorporate highly advanced Performance Cores that are optimized for single- threaded applications and highly Efficient Cores optimized for scaling multi-threaded workloads. The combination of these advanced cores dramatically increases performance and performance per watt.
Intel® Hybrid Technology - More Info
The Intel Core Processor (14th Gen), 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor and the 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor families represents a revolutionary leap forward in x86 processor design. Based on the Intel 7 manufacturing node, both generations "K" and "KF" series, incorporates a hybrid design that integrates both highly advanced Performance Cores that are optimized for single- threaded applications and highly Efficient Cores optimized for scaling multi-threaded workloads as well as managing background processes. The combination of these advanced cores that are present on the same die dramatically increases performance no matter the application type.
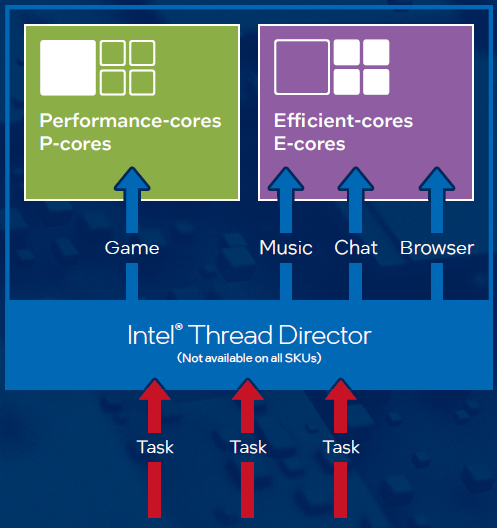
The key to successful implementation of a hybrid design is workload management and the determination of which instructions get sent to which core. Intel® Thread Director helps to monitor and analyze performance data in real-time to seamlessly place the right application thread on the right core and optimize performance per watt. That means gamers, creators, and professionals can harness both intelligence and power to enhance the experiences that matter most.
Performance-cores (P-cores)
The highest-performing CPU cores ever built by Intel, designed to handle single-threaded, lightly threaded, or burst workloads like 4kgaming and 3D design. (More info https://www.asipartner.com/solutions/gaming/12th-gen-intel-core-processors/)
Efficient-cores (E-cores)
Designed to handle multi-threaded and background tasks such as minimized browser tabs, IT services, and cloud syncing, leaving P-cores free to deliver incredible performance without interruption. (More info https://www.asipartner.com/solutions/gaming/12th-gen-intel-core-processors/)
Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor and 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor SKUs - More Info
ASI SKUs and comparison chart for the 14th, 13th and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ CPUs
| Intel Processor | ASI SKU |
|---|---|
| Core i9-14900K | 277851 / 277858 |
| Core i9-14900KF | 277852 / 277860 |
| Core i9-13900K | 266847 / 266855 |
| Core i9-13900KF | 266848 / 266856 |
| Core i9-12900K | 257292 / 257242 |
| Core i9-12900KF | 257293 / 257243 |
| Core i7-14700K | 277853 / 277861 |
| Core i7-14700KF | 277854 / 277862 |
| Core i7-13700K | 266849 / 266857 |
| Core i7-13700KF | 266850 / 266858 |
| Core i7-12700K | 257294 / 257240 |
| Core i7-12700KF | 257295 / 257241 |
| Core i5-14600K | 277855 / 277859 |
| Core i5-14600KF | 277857 / 277856 |
| Core i5-13600K | 266851 / 266859 |
| Core i5-13600KF | 266854 / 266860 |
| Core i5-12600K | 257296 / 257238 |
| Core i5-12600KF | 257298 / 257239 |
| Intel Processor | Cores (P+E) | Threads | P-Core Base / Boost (GHz) | E-Core Base / Boost (GHz) | Cache (L2/L3) | Memory | Watt BTP / MTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i9-14900K / KF | 24 (8P+16E) | 32 | 3.2 / 6.0 | 2.4 / 4.4 | 64MB (32+36) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 253W |
| Core i9-13900K / KF | 24 (8P+16E) | 32 | 3.0 / 5.8 | 2.2 / 4.3 | 64MB (32+36) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 253W |
| Core i9-12900K / KF | 16 (8P+8E) | 24 | 3.2 / 5.2 | 2.4 / 3.9 | 44MB (14+30) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 125W / 241W |
| Core i7-14700K / KF | 16 (8P+12E) | 28 | 3.4 / 5.6 | 2.5 / 4.3 | 61MB (28+33) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 253W |
| Core i7-13700K / KF | 16 (8P+8E) | 24 | 3.4 / 5.4 | 2.5 / 4.2 | 54MB (24+30) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 253W |
| Core i7-12700K / KF | 12 (8P+4E) | 20 | 3.6 / 5.0 | 2.7 / 3.8 | 37MB (12+25) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 125W / 190W |
| Core i5-14600K / KF | 14 (6P+8E) | 20 | 3.5 / 5.3 | 2.6 / 4.0 | 44MB (20+24) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 181W |
| Core i5-13600K / KF | 14 (6P+8E) | 20 | 3.5 / 5.1 | 2.6 / 3.9 | 44MB (20+24) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-5600 | 125W / 181W |
| Core i5-12600K / KF | 10 (6P+4E) | 16 | 3.7 / 4.9 | 2.8 / 3.6 | 29.5MB (9.5+20) | DDR4-3200 / DDR5-4800 | 125W / 150W |
Download here: 14th, 13th and 12th Gen Intel Core CPU Comparison and SKU Chart
Intel Thread Director - More Info
The key to successful implementation of a hybrid design is workload management and the determination of which instructions get sent to which core. The advanced intelligent tool that manages this complex process and does it at nanosecond speed is a feature called Intel Thread Director which is a hardware solution integrated in all Alder Lake processors. Intel Thread Director monitors the instruction mix of each thread, provides feedback to the OS to optimize scheduling decisions of the workflow, and dynamically adapts guidance to help the OS assign tasks. Although Intel Thread Director can work with Windows 10, it will have better optimization with Windows 11 making that the ideal OS for a new system using either the Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor or 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor.
Intel Hybrid Technology
Intel developed Performance-cores and Efficient cores to optimize workload demands, advance the PC industry, and enable new platform designs. Combined with Intel’s deepened co-engineering with our partners, these processors unlock the potential for innovative future use cases.
Performance-cores (P-cores)
The highest-performing CPU core ever built by Intel, designed to handle single-threaded, lightly threaded, or burst workloads like 4K gaming and 3D design.
Efficient-cores (E-cores)
Designed to handle multi-threaded and background tasks such as minimized browser tabs, IT services, and cloud syncing, leaving P-cores free to deliver incredible performance without interruption.
Designed to handle multi-threaded and background tasks such as minimized browser tabs, IT services, and cloud syncing, leaving P-cores free to deliver incredible performance without interruption.
Windows 11 SKUs
258004 - Microsoft Windows 11 Home 64-bit
258003 – Microsoft Windows 11 Pro 64-bit
New LGA1700 Socket - More Info
The 14th, 13th and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor family is based on a completely new architecture which includes a brand new LGA1700 CPU socket (Socket-V). Both the mounting hole design on the board and the height of the CPU combined with the socket have changed. The new mounting mechanism requires a newly designed cooling solution supportive of the LGA1700 mount holes or some vendors may provide an adapter allowing non LGA1700 fans to be converted to connect to the new socket. Box Retail package versions of the 14th, 13th and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor include an Intel heat sink fan solution, Laminar, specifically designed for the LGA1700 socket.
Follow the link below to a list of LGA1700 compatible heatsinks and adapters.
Intel Killer WiFi 6E - More Info
The Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor family and Intel 700 as well as Intel 600 series chipset support WiFi 6E which is the expanded version of WiFi 6. The biggest improvement is that WiFi 6E is open to use the 6GHz band where as WiFi 6 uses 2.4GHz to 5GHz. The expansion to the 6GHz band quadruples the number of available airways allowing for up to seven 160MHz channels which reduces signal interference and congestion. WiFi 6E improves network performance providing greater than 1Gbps performance and delivers lower latency of less than 1 millisecond. WiFi 6E is backward compatible with older devices but does require a WiFi 6E router to take advantage of the new performance capabilities.
WiFi 6E Routers
ASUS ROG Rapture GT-AXE11000 (SKU 251723)
TP Link Archer AX206 (SKU xxxxxx)
Intel 600 and 700 Series Chipset - More Info
The 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor uses Intel’s 600 Series chipset that supports the advanced processor features such as DDR5 memory, PCIe Gen 5.0, Thunderbolt 4 and more. Chipsets will include the Z690 (Gaming), Q670 (Business), H670 (Mainstream), B660 (Budget), and H610 (Entry). Although originally designed for the 12th Gen Intel Core Processor, motherboards that use the Intel 600 series chipset can also support the 14th and 13th Gen Intel Core Processor, with a BIOS upgrade, as both processors are compatible with the LGA1700 socket.
The Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen) and 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor families use Intel’s 700 Series chipset but can also be installed on an Intel 600 Series chipset motherboard but doing so will restrict some of the features to the maximum that is available with the Intel 600 series. The Intel 700 series supports the same advanced processor features such as DDR5 memory, PCIe Gen 5.0, Thunderbolt 4 and more. Chipsets will include the Z790 (Gaming), Q770 (Business), H770 (Mainstream), B760 (Budget), and H710 (Entry).
Raptor Lake Refresh, Raptor Lake and Alder Lake Motherboard Connectivity
| PCH Connectivity (up to) | 700-series (14th, 13th Gen Intel Core Processor) | 600-series (12th Gen Intel Core Processor) |
|---|---|---|
| PCIe 5.0 | 16 | 16 |
| PCIe 4.0 | 20 | 12 |
| PCIe 3.0 | 8 | 16 |
Raptor Lake Refresh, Raptor Lake and Alder Lake Processor PCIe
| CPU PCIe | 14th, 13th Gen Intel Core Processor | 12th Gen Intel Core Processor |
|---|---|---|
| PCI3 5.0 | 16 | 16 |
| PCIe 4.0 | 4 | 4 |
Intel 12th Gen Motherboard SKU chart
PCIe Gen 5.0 - More Info
The 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor was the first in the industry to support PCIe Gen 5.0 by offering up to 16 PCIe 5.0 and 4 PCIe 4.0 lanes. The 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor as well as the Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen) continue this tradition but have more advanced configuration options allowing the motherboard manufactures the ability to split the 16 PCIe 5.0 lanes creating more CPU direct M.2 SSD ports.
The true benefit of PCIe 5.0 is performance which is measured in three ways including gigatransfers, bandwidth, and frequency each of which double from one generation of PCI to the next. This means PCIe Gen 5.0 has a gigatransfer rate of 32GT/s, bandwidth of 128GB/s and a frequency of 32GHz all of which are double that of PCIe Gen 4.0 As with all generations of PCIe, the slots are backward as well as forward compatible. Both the 13th Generation Intel® Core™ processor and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ processor family includes 16 PCIe Gen 5.0 lanes and four PCIe 4.0 for a total of 20 CPU lanes.
Power Supply Info - More Info
The Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor and 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor motherboards will use standard power supplies based on the form factor of the chassis. While the “K” and “KF” versions of processors have a TDP rating of 125W, they do experience peak draws of up to 253W. These max power ratings occur for very short durations when the processor enters Max Turbo mode. It is therefore suggested that a standard system should include no less than a 550-650W PSU. Users who add discreet graphics cards to their builds should look to increase the power supply to 850W for a 3070/3060 class GPU or 1000W for a 3090/3080 or 4090/4080 class GPU.
Please verify power requirements for all of your system hardware before choosing a power supply for the system.
DDR5 Memory - More Info
The Intel® Core™ Processor (14th Gen), 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor as well as the 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor will support either DDR5 or DDR4 memory but not both on the same board. Memory support is determined by the MB manufacture. With a different pinout, DDR5 offers several key advantages over DDR4 which include 50% higher bandwidth going from 4.8Gbps to 6.4Gbps resulting in performance gains up to 87%. In addition, DDR5 draws slightly less power and supports higher density DIMMs allowing for up to 512GB of memory on a standard board.
DDR4 vs DDR5 - More Info
DDR5 has higher speeds and additional bandwidth, but that's not the only difference between the different memory types. Although DDR4 and DDR5 both use a 288-pin configuration, the pin traces are routed completely different to support the technical advances available with DDR5 and the notch patterns are in different positions so physically the two memory types are not compatible.
DDR5 modules operate at 1.1V compared to DDR4 which uses 1.2V. In addition, DDR5 contains on-module voltage regulation compared to DDR4 which utilizes voltage regulation from the mainboard. The onboard voltage regulator allows for more reliable and consistent power which is necessary to support the larger capacity modules.
In addition to on module voltage regulation, DDR5 also has on die ECC which corrects bit errors that occur on the memory. This is slightly different from ECC memory which correct bit at a system level including when data is in transit. The on-die ECC feature allows for more reliable memory performance as the capacities increase.
While DDR5 provides many new technical advantages, DDR4 also delivers benefits and value for both 13th and 12th Gen Intel Core Processor based systems.
Backwards compatibility: DDR4 based 14th, 13th and 12th gen motherboards can reuse memory modules that were in prior generation systems (as long as they were also using DDR4 modules). This will lessen the cost of upgrading your clients' systems and will allow for the repurposing of existing memory in new builds.
Performance needs: Depending on the primary use of the end clients PC, DDR4 may still provide solid performance when paired with a 13th Gen Intel Core processor or 12th Gen Intel Core processor.
Max Memory Speeds: While 14th, 13th and 12th Gen Intel Core Processor support both DDR4 and DDR5 memory, the 14th and 13th Gen Intel Core Processor use DDR5-5600 DRAM while the 12th Gen Intel Core Processor uses DDR5-4800 as its maximum speed of memory. All processors support up to DDR4-3200.
Thunderbolt 4.0 - More Info
Thunderbolt 4 doesn’t add increased bandwidth over Thunderbolt 3 like you may expect as both do 40Gbps. Thunderbolt 4 does however offer several improvements including the ability to connect two 4K displays or one 8K display whereas Thunderbolt 3 could only support one 4K display.
What’s New with Thunderbolt 4?
- Speed. Thunderbolt 4 ports have the same high-speed 40Gbps bandwidth as Thunderbolt™ 3. However, minimum PCIe data requirements have increased from 16Gbps to 32Gbps. This means that high-speed external PCIe devices like storage and external graphics could see significant increases in transfer rates and performance.
- Security. VT-d based DMA protection helps prevent security threats by remapping requests from external devices and checking for proper permissions.
- Wake from sleep. This feature allows a PC to be brought out of hibernation with peripherals that are connected through a dock.
