
The 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor ushered in a revolutionary leap forward in x86 processor design with the introduction on Intel’s hybrid architecture that integrates both highly advanced Performance Cores optimized for single threaded applications and highly advanced Efficiency Cores optimized for scaling multi-threaded workloads all on one die. Based on the Intel 7 manufacturing node, the new hybrid design was incorporated in “K” and “KF” versions on the 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor, and now has additional technical enhancements that have been extended in to the 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor. With both family of processors, the combination of these advanced cores dramatically increases performance and performance per watt no matter the application type.
In addition to introducing the new hybrid architecture, the 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor also was the first to include support for DDR5 memory, PCIe Gen 5, and Thunderbolt 4. The 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor continues the legacy of supporting these technologies, but includes other enhancements to the processor such as higher core count with the addition of more Efficiency Cores, support for faster DDR5 memory, up to 5.8GHz performance, and larger cache.
The combination of all these enhancements included in the 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor delivers a 15% gain in single threaded application performance, as well as a 41% gain in multi-threaded performance compared to the 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor.
13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor Enhancements
- Up to 8 Additional Efficiency Cores Boosting performance in Multi-threaded workloads
- Up to 5.8GHx Max Turbo Mode for Performance cores increasing performance for single threaded applications such as gaming
- 3X increase in L2 cache increasing up to 32MB
- 20% increase in L3 cache for up to 36MB
- Support for DDR5-5600 memory up from DDR5-4800.
- Continued support for DDR4-3200 memory based on the motherboard design
- Enhanced Over-Clocking including Per Core Tuning and Efficient Thermal Velocity Boost
Both Processors (12th and 13th Gen Intel Core Processor)
- 20 PCIe lanes including 16 PCIe 5.0 and 4 PCIe 4.0
- LGA1700 Socket (Socket V)
- Intel 600 Series Chipset (12th Gen Intel Core Processor and 13th Gen Intel Core Processor with a BIOS update)
- Intel 700 Series Chipset (13th Gen Intel Core Processor)
Processor Options
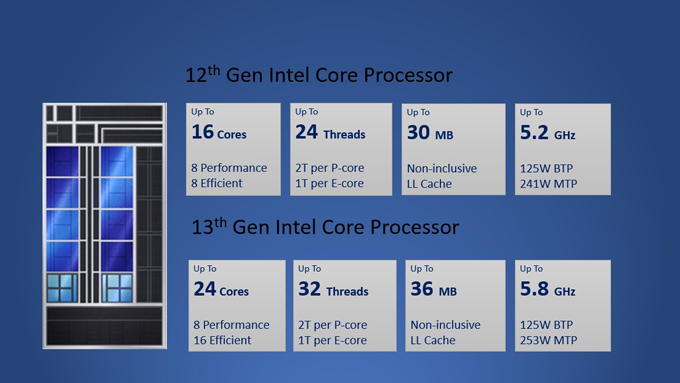
The 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor is available in Core i9, Core i7, and Core i5 versions with up to 16 Cores (8 Performance and 8 Efficient Cores), 24 threads (2 Threads per Performance Core and 1 Thread Per Efficient Core), up to 30MB of L3 Cache and up to 5.2GHz max clock speed.
The 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor is available in Core i9, Core i7, and Core i5 versions with up to 24 Cores (8 Performance and 16 Efficient Cores), 32 threads (2 Threads per Performance Core and 1 Thread Per Efficient Core), up to 36MB of L3 Cache and up to 5.8GHz max clock speed.
| Intel Processor | Cores (P+E) | Threads | P-Core Base/Boost | E Core Base/Boost | Cache (L2/L3) | Memory | Watt BTP / MTP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Core i9-13900K/KF | 24(8P+16E) | 32 | 3.0/5.8 | 2.2/4.3 | 64MB(32+36) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-5600 | 125W/253W |
| Core i9-12900K/KF | 16(8P+8E) | 24 | 3.2/5.2 | 2.4/3.9 | 44MB(14+30) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-4800 | 125W/241W |
| Core i7-13700K/KF | 16(8P+8E) | 24 | 3.4/5.4 | 2.5/4.2 | 54MB(24+30) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-5600 | 125W/253W |
| Core i7-12700K/KF | 12(8P+4E) | 20 | 3.6/5.0 | 2.7/3.8 | 37MB(12+25) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-4800 | 125W/190W |
| Core i5-13600K/KF | 14(6P+8E) | 20 | 3.5/5.1 | 2.6/3.9 | 44MB(20+24) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-5600 | 125W/181W |
| Core i5-12600K/KF | 10(6P+4E) | 16 | 3.7/4.9 | 2.8/3.6 | 29.5MB(9.5+20) | DDR4-3200/DDR5-4800 | 125W/150W |
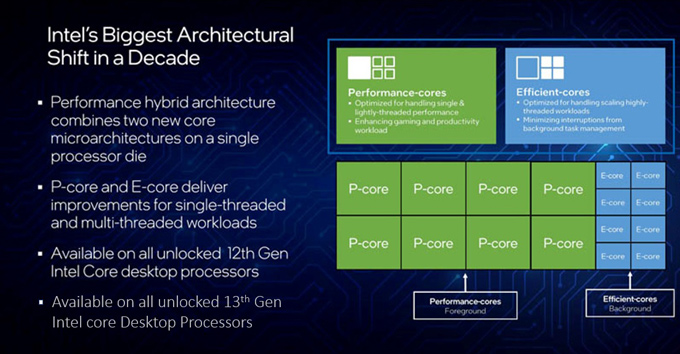
Performance Cores (P-Cores)
The 12th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor and 13th Gen Intel® Core™ Processor are made up of two types of cores. The first are the performance cores, which are the traditional high Ghz hyperthreaded style we are all familiar with from previous CPU generations. Performance cores are optimized for high performance single threaded applications. The new performance cores however are not just a slightly improved version of the previous core generation, the core is a completely redesigned architecture that includes a 1000GB/s compute fabric that ties the processor clusters as well as the individual cores together, and adds Intel Smart Cache, which shares the L2 and L3 cache among the core clusters to improve cache capacity and reduce latency. Other changes include increasing the out of order scheduler, adding more physical registers, and increasing the execution ports.
Efficient Cores (E-Cores)
The second type of core engineered in Alder Lake and Raptor Lake are smaller single threaded (No Hyper Thread Support) efficiency cores or E-Cores. Efficiency cores are a completely redesigned microarchitecture based on Intel’s Atom family of processors to optimize multi-threaded workloads that benefit from more cores rather than higher frequency cores. With the 13th Gen Intel Core Processor, code named Raptor Lake, Intel has increased the number of E-Cores by up to eight depending on whether the processor is a Ci5, Ci7 or Ci9.
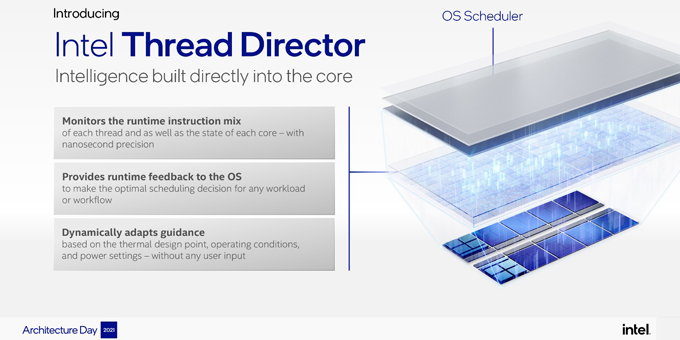
Intel Thread Director
The key to successful implementation of a hybrid design is workload management and the determination of which instructions get sent to which core. The advanced intelligent tool that manages this complex process and does it at nanosecond speed is a feature called Intel Thread Director, which is a hardware solution integrated in all Alder Lake and Raptor Lake processors. Intel Thread Director monitors the instruction mix of each thread, provides feedback to the OS to optimize scheduling decisions of the workflow, and dynamically adapts guidance to help the OS assign tasks. Although Intel Thread Director can work with Windows 10, it will have better optimization with Windows 11, making that the ideal OS for a new system based on with the 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor or 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor.
Cache
With the introduction of Intel’s Hybrid Architecture on the 12th Gen Intel Core Processor also came a technically advanced cache structure that included up to 30MB of L3 cache that is shared as well as 1.25MB of L2 Cache per P-Core and 2MB of L2 Cache per E-Core. With the 13th Gen Intel Core Processor, the L3 Cache is increased by up to 6MB for a maximum of 36MB. The L2 cache is also increased to 2MB per P-Core and 4MB per E-Core. The additional cache helps keep all the cores fed with data and reduces traffic helping to improve performance and increase IPC.
DDR5 or DDR4 Memory
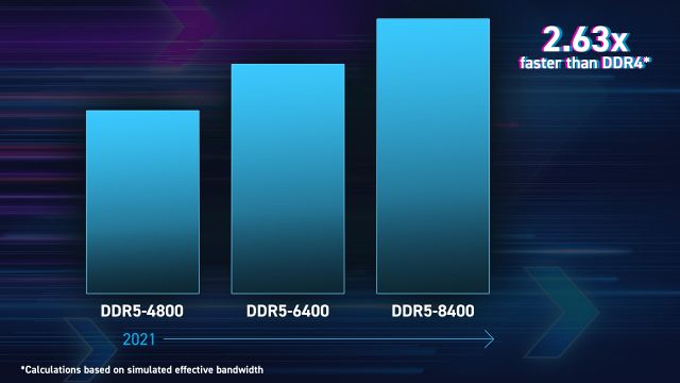
The 12th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor is the first to market with support for DDR5 memory. This support continues 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor. With a different pinout, DDR5 offers several key advantages over DDR4 which include 50% higher bandwidth going from 4.8Gbps to 6.4Gbps resulting in performance gains up to 87%. In addition, DDR5 draws slightly less power and supports higher density DIMMs which will reach 128GB per module. Currently DDR5 modules are available in 8,16 and 32GB allowing for up to 512GB of memory on a standard board. DDR5 also includes on-die ECC designed in to support the larger capacity DIMMS. In addition, the Power Management IC is integrated in to the DDR5 module moving that function off the motherboard and creating more efficient, and consistent voltage regulation. For added flexibility, both the 12th and 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor will support either DDR5 or DDR4 memory, but not both on the same board so memory support is ultimately determined by the MB manufacture. We expect board suppliers to offer a wide range of motherboards with different chipsets and different memory support options so resellers can select the best price performance option for their end clients.
PCI Gen 5.0
The 12th and 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor also supports an industry first PCIe Gen 5.0. PCIe performance is measured in three ways which include giga transfers, bandwidth, and frequency, each of which double from one generation of PCI to the next. This means PCIe Gen 5.0 has a giga transfer rate of 32GT/s, bandwidth of 128GB/s and a frequency of 32GHz all of which are double that of PCIe Gen 4.0 As with all generations of PCIe, the slots are backward as well as forward compatible. The 12th and 13th Generation Intel® Core™ processor family can support up to 16 PCIe Gen 5.0 and up to 4 PCIe Gen 4.0.
Overclocking
The 12th Gen Intel Core Processor introduced many new capabilities and overclocking features which have been enhanced for the 13th Gen Intel Core Processor. The new 13th Generation model includes new per core tuning virtualizations using Intel Extreme Tuning Utility and has a simplified Intel Speed Optimizer. Additionally the 13th Gen Intel Core Processor includes memory overclocking capability for both DDR4 and DDR5 memory which can be done with 1 click.

Thunderbolt 4.0
Thunderbolt 4 doesn’t add increased bandwidth over Thunderbolt 3 like you may expect as both do 40Gbps. Thunderbolt 4 does however offer several improvements including the ability to connect two 4K displays or one 8K display whereas Thunderbolt 3 could only support one 4K display.
Wifi 6E
The 12th and 13th Generation Intel® Core™ Processor family, as well as the Intel 600 and 700 series chipset, support WiFi 6E which is the expanded version of WiFi 6. The biggest improvement is that WiFi 6E is open to use the 6GHz band whereas WiFi 6 uses 2.4GHz to 5GHz. The expansion to the 6GHz band quadruples the number of available airways allowing for up to seven 160MHz channels which reduces signal interference and congestion. WiFi 6E improves network performance providing greater than 1Gbps transfer and delivers lower latency of less than 1 millisecond. WiFi 6E is backward compatible with older devices but does require a WiFi 6E router to take advantage of the new performance capabilities.

